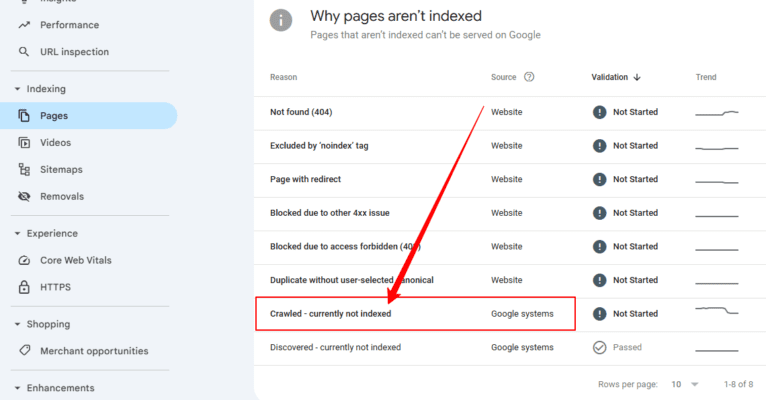
When you see the status of ‘Crawled’ and ‘currently not indexed’ in Google Search Console, it can be very confusing and frustrating. Google has visited your page, though it is not yet in the index and will not appear in search results.
This is a common happening even in well-run sites and does not imply that the site has been punished. Google often struggles to decide whether a page should be indexed.
This guide will explain what the status means, why it is this way, and how you can safely fix it in 2026.
What Does “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” Mean?
-
Googlebot successfully crawled the page
-
No technical blocking exists (robots.txt, noindex, etc.)
-
Google decided not to index it (for now)
This is a quality and value assessment, not a technical error.
Is “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” Bad for SEO?
Not necessarily.
Google delays indexing when:
-
Content doesn’t add enough unique value
-
Similar pages already exist
-
The site has limited crawl or quality signals
However, if essential pages remain in this state for a long time, it can affect organic growth and visibility.
7 Common Reasons Google Crawls but Doesn’t Index Pages
1. Thin or Low-Value Content
Pages with:
-
Very short content
-
Generic information
-
No clear purpose
Often failsGoogle’ss quality threshold.
Fix:
Expand content with:
-
Original insights
-
Practical examples
-
Clear answers to user intent
Aim to be better, not longer.
2. Duplicate or Near-Duplicate Pages
If your page is similar to:
-
Other pages on your site
-
Existing indexed content
Google may choose one version and ignore the rest.
Fix:
-
Merge similar pages
-
Use proper canonical tags
-
Remove unnecessary variations
3. Weak Internal Linking
Pages with few or no internal links appear less important to Google.
Fix:
-
Link from high-authority pages
-
Use descriptive anchor text
-
Place links contextually within content
Internal linking helps Google understand priority and relevance.
4. Search Intent Mismatch
If your content doesn’t match what users are searching for, Google may delay indexing.
Example:
User intent = “how to fix indexing issues.
Your page = definition-only content
Fix:
Match the content format:
-
Guides for “how to” queries
-
Lists for comparison searches
-
Clear answers to questions
5. Poor Overall Site Quality Signals
If many pages on your site:
-
Are thin
-
Remain unindexed
-
Have low engagement
Google may slow indexing across the site.
Fix:
-
Improve overall content quality
-
Remove low-value pages
-
Strengthen E-E-A-T signals
6. Crawl Budget Limitations
Large websites or new sites may face crawl prioritization issues.
Google crawls more valuable pages first.
Fix:
-
Remove unnecessary URLs
-
Optimize sitemap
-
Focus on quality over quantity
7. Recently Published or Updated Content
Sometimes the page is too new.
Google may revisit and index it later if quality signals improve.
Fix:
-
Be patient
-
Improve content
-
Build internal links
-
Request indexing (once, not repeatedly)
How to Fix “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” (Step-by-Step)
-
Improve content depth and uniqueness
-
Check for duplication and canonicals
-
Add strong internal links
-
Ensure the page satisfies search intent
-
Remove low-quality pages sitewide
-
Update and resubmit sitemap
-
Use URL Inspection → Request Indexing (sparingly)
How Long Does Google Take to Index Crawled Pages?
There is no fixed timeline.
-
Some pages index within days
-
Others take weeks or months
-
Some may never be indexed
Indexing depends on quality, relevance, and site trust.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Repeatedly requesting indexing
-
Publishing mass low-quality pages
-
Keyword stuffing to “force” indexing
-
Copying content from other sites
-
Ignoring internal linking
These actions often make the problem worse.
Crawled vs Discovered – Currently Not Indexed
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Discovered – Not Indexed | Google knows the URL but hasn’t crawled it |
| Crawled – Not Indexed | Google crawled it but chose not to index it |
Both are quality-related, not penalties.
Final Thoughts
“Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” is Google asking for better content, not rejecting your site.
Instead of forcing indexing, focus on:
-
User value
-
Content clarity
-
Strong internal structure
When Google sees apparent usefulness, indexing usually follows.